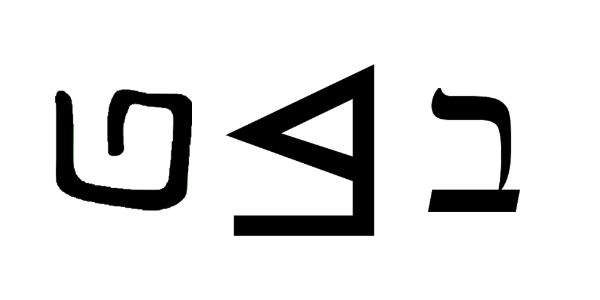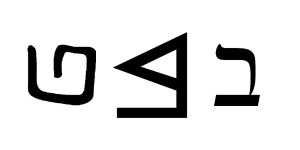« Back to Glossary Index
Synonyms:
𐤁
The letter 𐤁 (bayat) or B/b is the second letter in the Afroasiatic language known as Paleo-Hebrew (Ābarayat). The letter has been equated with the letter B and the letter V in the English language. However, the letter V is mostly associated with Modern Hebrew because of the sound, whereas it originally came from a branch of the Paleo-Hebrew letter we associate with U in the English language.
To read the study guide entry that elaborates on 𐤁 (b) then visit https://www.paleohebrewdictionary.org/ext/b or use phdict.org/ext/b to share a short link with others.